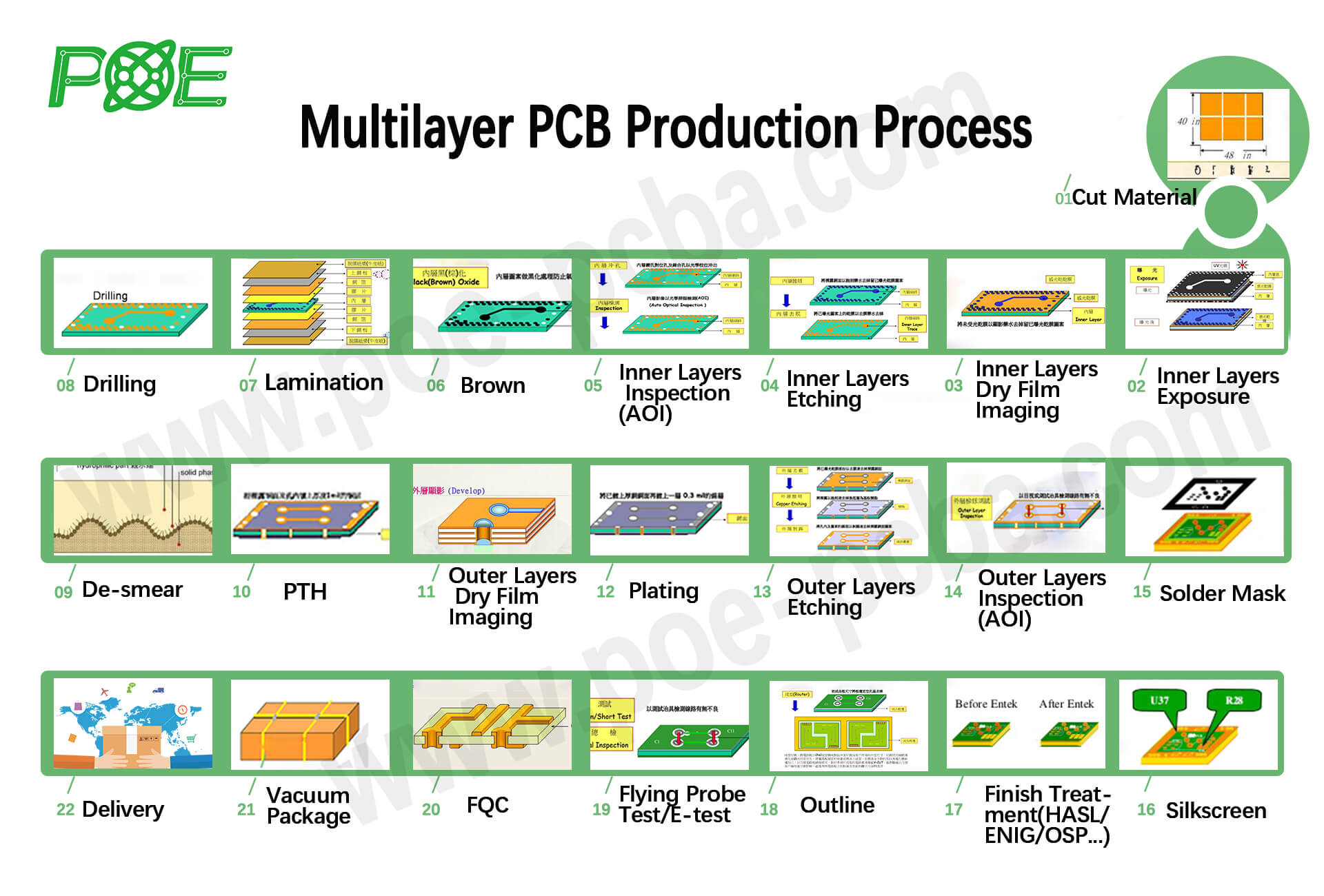
Multilayer PCB
With the continuous innovation of electronic technology and the continuous improvement of the requirements for electronic equipment in some industries such as computers, medical treatment, and aviation, printed circuit boards are developing in the direction of smaller volume, lighter weight, and increased density. Single and double-sided printed boards can no longer meet the demand, so it is necessary to consider using more layers and higher assembly density multilayer circuit boards.
What is a multilayer circuit board?
In daily life, multilayer PCB circuit boards are currently the most widely used circuit board type. Multilayer PCB are circuit boards composed of two or more conductive layers (copper layers) superimposed on each other. The most common is four Six-layer board, such as the familiar computers in our daily life. Single-layer and double-layer boards are easy to distinguish and can be distinguished with the naked eye. Hold the board and look at the light. Except for the wiring on both sides, the rest of the place is transparent . But for multilayer PCB boards with four-layer boards and six-layer boards, if there is no corresponding mark on the board, it is not so easy to distinguish. Generally, the requirements for the structure design and process production of multilayer electric boards are very high, and the higher the number of layers, the more difficult it is, and it is suitable for use in more complex circuits.
Advantages of Multilayer PCB
Multilayer PCBs offer a range of significant advantages, making them the first choice for the design of modern electronic devices.
1. High-density design
Multilayer PCB allows high-density circuit design in limited space. This is particularly important for modern electronic devices such as smartphones, tablets and computer motherboards that require complex circuitry and multi-functions.
2. Better electrical performance
Due to the combination of inner and outer layers, multi-layer PCBs enable shorter signal paths, thereby reducing signal delays and interference. This is especially critical for high frequency and high speed circuits.
3. Enhanced heat dissipation performance
The insulating layer and conductive layer in the middle of the multi-layer PCB can effectively dissipate heat, prevent components from overheating, and improve the reliability and life of the system.
4. Electromagnetic compatibility
By properly designing the layer stack and ground layer, multi-layer PCB can effectively shield electromagnetic interference (EMI) and improve the stability and reliability of the circuit.
Disadvantages of Multilayer PCB
Although multilayer PCBs offer numerous advantages, there are also some disadvantages.
1. High manufacturing cost
The manufacturing process of multi-layer PCB is complex and involves multiple steps of lamination, lamination and drilling, so the cost is high. Especially for PCBs with more layers, the cost will increase significantly.
2. Design complexity
The design of multi-layer PCB requires precise layer stacking and layout planning, which makes the design difficult. This requires designers to have extensive experience and expertise.
3. Difficulty in maintenance
Due to the complex structure of multi-layer PCBs, once a failure occurs, repair and replacement become more difficult and expensive.
A typical multilayer PCB consists of the following parts:
Inner layer circuit board:The middle conductive layer, usually made of copper.
Insulation layer: The insulating material between the layers, usually epoxy or other high dielectric materials.
Surface circuit board: The outermost conductive layer used to connect external components.
Vias: The conductive path connecting the layers.
Application advantages of multilayer PCB circuit boards: Multilayer PCB is widely used in various fields, especially in occasions where high performance and high density circuits are required.
Consumer electronics
Devices such as smart phones, tablets, and laptops rely on multilayer PCBs to achieve their complex functions and compact designs.
Communication equipment
Communication equipment such as routers, switches, and base stations need to process a large amount of data and signals, and multilayer PCBs can provide the required high reliability and high performance.
Medical equipment
Multilayer PCB is used in medical equipment for high-precision and high-reliability circuit design, such as MRI, CT scanners, and electrocardiographs.
Automotive electronics
Navigation systems, in-car entertainment systems, and advanced driver assistance systems (ADAS) in modern cars all rely on multilayer PCBs to achieve their complex functions.
Industrial control
Multilayer PCB is widely used in industrial automation and control systems, such as PLC (programmable logic controller), inverters, and robot controllers.
When designing and manufacturing multilayer PCBs, the following technical parameters are usually considered:
Number of layers: usually between 4 and 12 layers, and special applications may require more layers.
Board thickness: ranging from 0.4 mm to 3.2 mm.
Minimum line width/line spacing : usually between 0.1 mm and 0.2 mm.
Aperture: The diameter of the through hole is usually between 0.1 mm and 0.5 mm.
Material: FR4, ceramic, polyimide and other materials are commonly used.
Multilayer PCB has become an indispensable part of modern electronic devices with its high density, high performance and complex circuit design capabilities. Despite its high manufacturing cost and design complexity, its wide application in consumer electronics, communication equipment, medical equipment, automotive electronics and industrial control has fully demonstrated its value and importance. Through continuous technological innovation and optimization, multilayer PCB will continue to play an important role in the electronics industry.