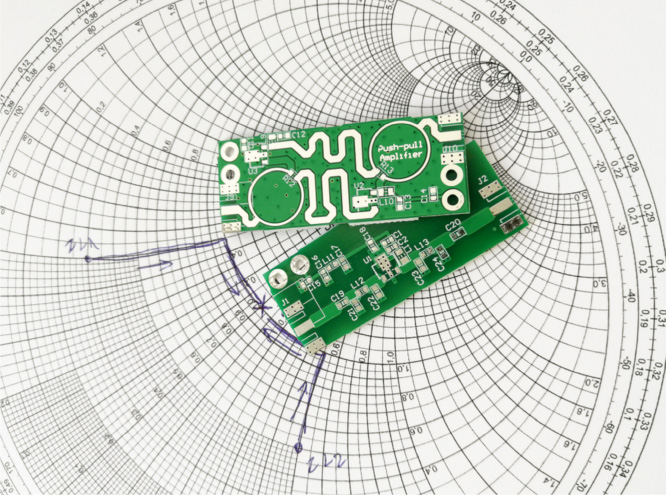
Impedance control (EImpedance Controlling), there will be a variety of signal transmission in the conductors in the circuit board, to increase its transmission rate must increase its frequency, if the line itself due to etching, stack thickness, wire width, and other different factors, will The impedance is worth changing, and the signal is distorted. Therefore, the impedance value of the conductor on the high-speed circuit board should be controlled within a certain range, called "impedance control".
The impedance of the PCB trace will be determined by its inductive and capacitive inductance, resistance, and conductance. The main factors that affect the impedance of the PCB traces are the width of the copper line, the thickness of the copper line, the dielectric constant of the medium, the thickness of the medium, the thickness of the pad, the path of the ground line, and the traces around the trace. PCB impedance ranges from 25 to 120 ohm.
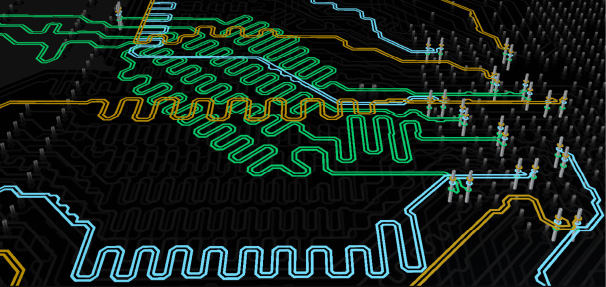
In practical situations, PCB transmission lines usually consist of a wire trace, one or more reference layers, and insulating materials. Traces and slabs constitute the control impedance. PCB will often adopt a multi-layer structure, and the control impedance can also be constructed in various ways. However, no matter what method is used, the impedance value will be determined by its physical structure and the electronic properties of the insulating material:
Width and thickness of the signal trace Height of the core or pre-filled material on both sides of the trace Configuration of traces and slabs Insulation constant of core and pre-filled material