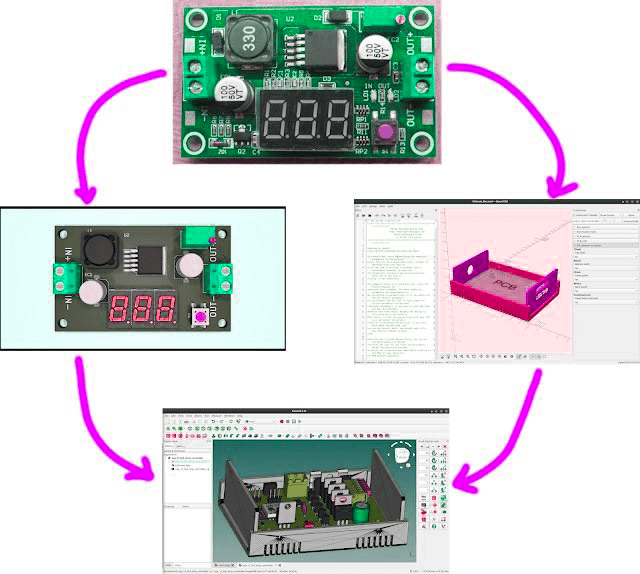
3D printing is a process of manufacturing physical objects from a 3D digital model, usually by laying down many continuous thin layers of material. It converts a digital object (its CAD representation) into a physical form by adding material layer by layer. There are several different techniques to 3D print objects. 3D printing, whether on an industrial, local, or personal level, brings many benefits that traditional manufacturing (or prototyping) methods simply cannot provide.
The 3D printing process allows mass customization-the ability to personalize products according to individual needs and requirements. Even in the same building room, the nature of 3D printing means that a large number of products can be manufactured at the same time according to the requirements of the end user, without additional process costs. 3D printing is also becoming an energy-saving technology, it can provide environmental efficiency in the manufacturing process itself, using up to 90% of standard materials, thus reducing waste, and through lighter and stronger during the entire operation of additive manufacturing products the design, compared with traditionally manufactured products, has a smaller carbon footprint.
For industrial manufacturing, one of the most cost, time, and labor intensive stages in the product development process is the production of tools. For small and medium-volume applications, industrial 3D printing (or additive manufacturing) can eliminate the need for tool production, thereby eliminating the costs, delivery time, and labor associated with it. This is an extremely attractive proposal, and more and more manufacturers are taking advantage of this proposal.